The pension system has existed in the United Kingdom since 1908. In this country, for the first time in Europe, a system was introduced that provided an individual approach to each pensioner. A pension in the UK provides elderly people who have retired, along with very favorable conditions for a quiet life, also various benefits and benefits. Even the global crisis did not affect the size of pensions in Foggy Albion. And this is quite natural.
Pension reform in the UK
In 2020, another reform of the UK pension system was carried out. Many key provisions have been adjusted. How the retirement age and its size have changed will be discussed in more detail below, but now let’s focus on one interesting point.
According to the innovations, persons who have reached 55 years of age have the right to fully withdraw the pension savings in their account by carrying out just one banking transaction. Moreover:
- no tax is paid on the first 25% of withdrawals;
- the remaining amount is subject to income tax.
Before the reform, most pensioners could have a constant source of funds until the end of their days. However, some of them decided not to prolong the pleasure.
In particular, there was a case when a person, having retired, immediately spent 120 thousand dollars on cars, alcohol and a casino. This story served as one of the arguments in the debate between members of the UK Parliament about the relevance of making changes to the country's pension system.
Introduction
The pension system and the scale of the potential problem of population aging in the UK are very different from those in most European countries.
The problem of population aging will be less pressing over the next fifty years than in many other countries, and cost issues related to future pensions may be considered relatively less pressing. The private sector already plays an important role in pensions and has become increasingly important as a result of reforms in the 1980s. Over three-quarters of the working population is covered by some kind of private pension scheme, and even the pensions of current retirees are approximately 50 percent publicly funded (though for those in the bottom half of the income distribution the proportion is much higher). The purpose of this paper is to explain the nature of the reforms that transformed the UK pension system in the fifteen years after 1980, and to provide some preliminary assessment of these reforms. Before considering the reforms that have been implemented, their purpose and the extent to which that purpose has been achieved, we will give a brief history of the UK pension system and present its status in 1996.
Types of pensions in the United Kingdom
The UK pension system provides three main types of pensions.
- State pension - state pension. The current maximum basic state pension is: for a single person - £125.95 per week;
- for husband or wife based on the other spouse's National Insurance contributions - £73.30 per week. Persons who have ended family relationships and who have not entered into a new marriage, even a civil one, before retirement can also receive this amount.
Every year, in accordance with the dynamics of the consumer price index, the basic pension is indexed. The State Pension is not available to people who have worked in the UK for less than 10 years.
- Occupational pension - labor pension. It is formed from funds: the part of the income received by the employee transferred to the pension fund (hereinafter referred to as the PF);
- the amount deposited by the employer into the employee’s PF account.
The employment pension is not issued to UK residents/citizens who worked part-time or earned little.
- Private pension – private pension. The employee himself chooses the fund in which the funds transferred from his salary for pension are accumulated. Upon retirement, the person will receive the amount generated from the investment. There are many funds operating in the UK with different conditions for accumulating funds.
Old age pensions in England consist of two components: the main (basic) pension and an additional part.
All Britons who have reached retirement age can apply for a basic state pension. An additional portion is due for length of service.
In the 60s and 70s of the last century, the so-called final salary pension was widespread in Great Britain. At that time, most large companies offered it to their employees. People worked in one place all their lives, accumulated experience, and when they retired, they knew exactly how much the company would pay them every month.
Due to increasing life expectancy, such a pension has become unprofitable for companies. Therefore, it is now extremely rare.
Here's something else to consider when planning for retirement. It was said above that in the UK, along with the basic pension, an Additional State Pension is accrued. When calculating it, not only earnings are taken as initial data, but also information about the volume of NI contributions made by a person. So: self-employed people cannot receive Additional state pension.
Features of the pension system
By 2020, England underwent a reform of the pension system, during which the retirement age increased. A new type of contribution “New State Pension” has also appeared.
To receive the “New State Pension” you need:
- 10 years of work experience in the UK;
- 10 years of experience in receiving social insurance benefits for unemployment;
- voluntarily paid pension contributions.
If a citizen of England has worked for 35 years, he can count on the highest pension.
There are a number of benefits:
- The purchase of medicines and travel on public transport are provided free of charge.
- Discount on utility bills.
- Banks provide favorable conditions with high interest rates for maintaining savings accounts.
Attention! Persons born before April 6, 1945 are required to obtain 44 years of work experience. For the rest, the age of work experience is 30 years.
Working pension
Working citizens carefully choose their employer, because... the quality of cooperation directly affects pension contributions.
Work security in old age is added to the state one, and does not replace it. The employee contributes a percentage of his total income to accumulate a working pension. The employer then adds his percentage to the accumulated pension after a certain number of years. The amount that will be charged as a surcharge is agreed upon in advance. It depends on the company, the employer and the length of the employee’s work.
The entire amount is in an investment account, which, if everything goes well, is constantly increasing. Pension income is not taxed, so the pensioner receives the entire amount in hand.
You can count on a working pension:
- persons receiving at least £490 monthly;
- citizens earning at least £113 weekly;
- persons earning at least £452 in 4 weeks.
Anyone who earns less falls out of the workers' pension system.
Also, an employee counting on deductions must:
- be over 22 years old;
- be under the established retirement age;
- earn more than the specified minimum thresholds.
Pensioners have the right to withdraw their savings partially or all at once. The security can be divided over a specified number of years. If a citizen withdraws the entire amount, he is required to pay income tax on 75% of the deductions.
Important! Last salary security was previously popular. A citizen worked all his life at one enterprise, which until the end of his days paid him a certain amount. Now such payments have practically disappeared, because... they are disadvantageous for companies.
Private pension
A person can personally contribute a certain amount of income to a pension fund every month. The fund transfers funds to an investment account, which helps increase the final payout.
Once the payer reaches retirement age, he can withdraw all his money or divide the amount into monthly payments.
Fund accounts can be used by all UK citizens with at least 2 years of work experience. When withdrawing 25% from accounts, no income tax is paid.
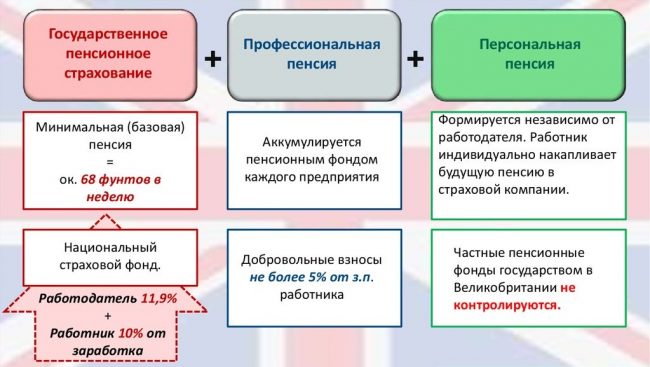
UK pension levels
The question of what the pension is in the UK in 2020 is of interest to many - not only potential migrants, but also local residents who have reached adulthood. Most of them know that in 2016, a reform of the pension system was carried out in the country and the real figures of pensions from the state have undergone changes.
First of all, it must be said that the minimum pension has increased, and significantly - by 33.7%. In particular, for a Briton who retired before 04/01/2016, it is £113.10 per week.
Residents of Foggy Albion who have received pensioner status since April 2020 are awarded a minimum of £155.65 per week, which in terms of the middle of the third quarter of 2020 is equal to 12,197 Russian rubles. For comparison: in the Russian Federation in 2020, the minimum pension was approved at the level of 8,846 rubles, not per week, but per month.
But the average pension in England is higher than the basic one. The fact is that the amount of financial assistance to older people from the state depends on many factors. For example, the longer the pension period, the greater the amount of payments. Every year of retirement increases an Englishman's income by £4.44 per week.
It is easy to calculate that with 5 years of pension service, an elderly person on average will receive £9,248.2 per year in the UK. In conversion, this amounts to 712,690 rubles per year, or almost 59,391 per month.
As for the maximum pension in the UK, its size is unlimited. To give you an idea of the order of numbers, here are just two examples.
- Former British Prime Minister Tony Blair receives £520.14 thousand per year during his well-deserved retirement (40,083,341 rubles). This is the largest pension in the world among former leaders of states.
- British Prime Minister Gordon Brown was entitled to approximately the same pension. But in January 2008, while in this position, he refused to apply for a pension in that amount after resigning. With this action, he called on parliamentarians to limit the increase in their salaries.
Other additional payments and benefits
The size of the pension is affected by various factors, including disability, military service, and widow status. Those injured during the Second World War are also entitled to a supplement. When calculating pensions for WWII veterans, military rank and the severity of injuries are taken into account (down to which finger was lost in battle).
The size of monthly payments ranges from 150,000 to 650,000 rubles.
Finally, there are many discounts, benefits and free services available to help seniors. The state helps pay for housing, medicine and transportation. The same situation is observed in other European countries. For example, in Germany, 98% of pensioners can live freely on their pension.
In these countries, older people can afford to buy new equipment and cars, lead an active lifestyle and travel a lot.
Retirement age in the UK
Since November 2020, the retirement age for men and women in the country has become the same - 65 years. Previously, men retired at the same 65 years, and women at 60 years. But the government will not stop there: it plans to raise the retirement age to 67 years.

However, specialists in some categories can retire at the age of 55. These are, for example, disabled people and workers in special fields of work.
Increasing the age limit is an objective necessity. After all, life expectancy in Foggy Albion for men is 79 years, and for women – 83 years. Thus, the shift in retirement dates is quite reasonable.
Nevertheless, British legislation allows for the option of early acquisition of pensioner status by a citizen of the country. This approach is practiced by people who, during their working career, have accumulated funds in an amount sufficient for a comfortable stay in a well-deserved rest.
And the state pension will be paid to them after their 65th birthday. At least until this age limit rises.
Cost containment
Degree of cost containment.
In the short, medium and long term, the most important contribution to cost containment is to maintain price-based indexation of the basic state pension. If pensions had been adjusted according to earnings since 1980, the cost of paying them would have been almost £36 billion in 1995-96. Art. (12% of all government spending) instead of 27 billion f. Art. Such an increase in spending would have limited benefits for the poorest pensioners, as evidenced by the fact that around £2 billion was saved through means-based payments. Art.
But even such savings seem insignificant when compared with the scale of savings in the future. The Government Actuarial Service estimates, begun in 1995, that the cost of a basic pension in constant pounds will reach £47 billion by 2030. Art. and will subsequently remain at this level. If earnings were indexed from 1995, costs would rise to £80 billion by 2030. Art., and by 2050 - up to 107 billion f. Art. If indexed by price, National Insurance contribution rates would remain virtually unchanged by 2030, but if indexed by earnings they would probably have to increase by ten percentage points. Of course, the most serious potential problem with this approach to cost containment is the significant deterioration in the standard of living of retirees in the future compared with other categories of the population.
Containing future costs was also a major consideration in the SERPS reforms introduced under the Social Security Act 1986. The Government Actuarial Service estimates that SERPS reform will reduce future costs to the extent that the National Insurance contribution rate could be reduced by three percentage points by 2033.
From a political point of view, it is interesting to note that all
savings from SERPS reform will occur in the future. The rights of those retiring before 2000 were not changed. Since the whole scheme is new, the cost before 2000 would not have been high in any case, and in 2000 it would be just over £4 billion. Art. Thus, older workers have no reason to oppose this reform. As a result of the 1986 reforms and further smaller measures introduced under the Pensions Act 1995, spending on SERPS will peak at £12 billion in 2030. Under the original scheme, costs by 2030 would be over £40 billion. Art. From Table 1 (see below) it is clear that savings due to reforms will not appear until 2020 or 2030, but they will be very noticeable.
Table 1. Financial results of the SERPS (£ billion 1994/95 prices)
| 1994/95 | 2000/01 | 2010/11 | 2020/21 | 2030/31 | |
| Initial scheme | 1,8 | 4,2 | 12,0 | 25,0 | 41,0 |
| After the Social Security Act of 1986 | 1,8 | 4,2 | 9,2 | 14,5 | 18,7 |
| After the Pensions Act 1995 | 1,8 | 4,2 | 8,4 | 10,9 | 12,0 |
The scale of the 1995 reforms was smaller than in 1986, but their main effect was also a reduction in future costs. The most significant change is the gradual equalization of the retirement age for men and women (65 years old) by increasing the retirement age for women by 6 months annually from 2010 to 2020. It is also very important to eliminate the provision on state financing of part of the indexation of professional pensions taking into account inflation in the event that the inflation rate exceeds 5%. The state has refused to provide insurance against such risks, and now it is borne by the employees themselves, pensioners and employers directly involved in the pension scheme.
Success and the Cost of Cost Containment
. On the face of it, the broad transfer of responsibility and costs to the private sector has been quite successful. The UK is virtually alone among the OECD countries where the tax burden is not expected to increase significantly in the future as a result of population aging. To a certain extent, this reflects a more favorable demographic situation compared to other countries. However, the most important factor is the determination with which the government undertook these reforms, analyzing possible problems in advance and addressing them in a radical and effective manner. While other European countries (e.g. France, Italy, Germany) began to address these problems only in the 1990s, when their scale became very significant, the UK government has consistently pursued policies since the 1980s aimed at preventing potential problems. From a political point of view, this is possible with
Required work experience
To be able to apply for a pension, you must confirm your work experience. Experts recommend carefully reading the calculation scheme for this indicator, finding out all the key parameters that influence it.
Qualifying years include:
- all years during which the employee had the status of employed;
- all years of employment in self-employed status, if National Insurance Contributions were paid;
- the period for which child benefit was provided, even if there was no work at that time;
- a period during which a person earned at least £155 per week.
Checking a person's pension status is done by making a request to the UK Government's HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). If the length of service for the minimum pension turns out to be insufficient, you can pay the missing insurance premiums, thus purchasing the necessary years.
State pension calculation
State financial assistance is paid to all citizens of the United Kingdom when they reach retirement age. Its value does not depend on length of service. But, as was said, the calculation takes into account the time spent on a well-deserved rest. The formula for calculating the state pension in the UK looks like this:
RGGP = (4.44 × PS + 155.65) ×52, where
- RGP - the amount of the annual state pension (in pounds sterling);
- PS – pension experience (years).
Thus, a man who turns 75 in 2029 will receive
(4.44 x 10 + 155.65) x 52 = £10,402.6/year.

This is the simplest example of calculating the British state pension. But its value is influenced, in addition to retirement experience, by some other factors, for example, widowhood, disability, and military service. To account for them, special tables with coefficients are used.
This approach is intended to increase the amount of financial assistance from the state, making the life of an elderly person more comfortable. As practice shows, the pension in the UK at £867 per month is sufficient for a normal life if a person has his own home. But this amount is clearly not enough to pay for the rent of the apartment,
Benefits for pensioners in the UK
The UK government has provided a variety of benefits for older people. Let's name just a few of them:
- favorable banking conditions, high interest rates on savings accounts;
- reduced tariffs for utilities. In particular, during the winter months there are significant discounts on heating;
- free travel on public transport;
- free provision of medicines prescribed by a doctor.
At the same time, all of the above does not allow us to give an unambiguous answer to the question of how pensioners live in England. It will not be possible to live without worries solely on a state pension. Yes, the government does not allow people on their well-deserved rest to live in poverty by providing various benefits. But in order to have a comfortable old age, a person must accumulate funds himself.
Foreign pensioners in the United Kingdom
Elderly foreigners, under certain conditions, can count on a special social benefit in the UK - Pension Credit. Older people have the right to receive such financial assistance even without a single day of work experience in the United Kingdom. You just need to have a residence permit, as well as proof of actual residence in the country.
The article “Residence permit, permanent residence, citizenship: concepts, features, differences” will help you understand the intricacies of the differences between statuses.

Pension Credit will increase a claimant/couple's weekly income to £155.65 per week for a single person or £243.25 for a couple.
Stateless immigrants have two options:
- when you reach old age, simply apply for the minimum Pension Credit benefit;
- earn enough experience to receive a state pension. In the UK it is 10 years.
The question may arise what foreigners who come to the country and work on a temporary or permanent basis receive. It all depends on the specific case.
If a foreigner has moved to the UK for permanent residence, works, pays taxes and transfers a certain amount each month into the National Insurance account, he is subject to all the rules regarding receiving a pension that apply to local residents.
In addition, by drawing up an employment contract, you can become a participant in the pension scheme of your employer. Another option is to open a personal pension plan with a private provider.
It may happen that a citizen of another country is planning to move to Foggy Albion at pre-retirement age, which is why he will not have time to obtain the length of service required for a state pension in the UK. Then he needs to make sure that it will be accrued in his home country.
Find out how pensions are paid for Russians living abroad in 2020.
If a foreigner lived in one of the EU states, he will be paid a pension in the amount to which he is entitled in accordance with the legislation of that country.
The article “Pension size in European countries” will tell you about the amount of contributions, retirement age and other issues related to the well-deserved rest of Europeans.
British pension benefits
The highest pension for 35 years of work experience is almost 650 pounds monthly or 52,000 rubles. For England these are not such large amounts.
A citizen with 10 years of work experience receives 170 pounds of contributions from the state monthly or 14,000 rubles.
Individual entrepreneurs do not receive contributions from their working pension. They must independently transfer part of the amount to the fund.
The British pension system does not provide for a wealthy old age; it is believed that an elderly person must independently take care of his quality of life in old age. The state only provides the minimum that will allow you to eat and pay bills.
How is pension calculated?
Providing for an Englishman consists of 3 points:
- government contributions;
- work deductions;
- personal savings.
The largest state pension is received by those who have worked for 35 years. Those who have worked for 10 years or more also receive payments, but the amount will be less.
Personal savings usually amount to 5-7% of the monthly salary. Some citizens can afford to save large sums.
If a citizen does not work but lives in England, he receives social benefits. The fact of residence within the country must be confirmed by relevant documents.
War veterans, disabled people and widowers receive additional contributions. Wounded veterans receive the most bonuses. There are additional benefits for all senior citizens, such as free medicines and travel.
It is also useful to read: Pension in Belgium
Minimum and maximum level
The smallest government provision is £44.40 weekly. To obtain it, you must have ten years of work experience in the UK. This is the minimum threshold, which can be increased by receiving financial assistance.
The government financial benefit is £142 per week, which already covers bills and food. All UK citizens over 66 years of age are eligible to receive financial assistance if their contributions are less than £160 per week.
The maximum state pension is £165 weekly.
Pension supplements
For older Englishmen, there is a Pension Credit, which is paid by compensating for the difference in minimum and actual payments. Anyone who has citizenship or a residence permit within the country can apply for Pension Credit, no matter how long the person has worked in England.
If a pensioner receives less than £160 weekly or RUB 13,000, and less than £243 or RUB 20,000 for a couple, they are eligible to receive payments.
Relying only on the state pension within the UK is quite risky. Therefore, citizens from a young age, when applying for a job, think about a working pension, choosing favorable conditions. Also, almost every Englishman has personal contributions to the fund.