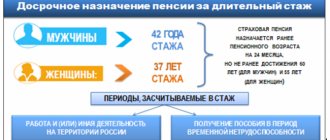
Duration of service in the army according to the recruit system
Initially in Rus', military service was not regulated by any laws of that time. Men had to defend their homes and perform military duty only in times of danger to the state.
The first obligation of Russians to serve in the army appeared only during the reign of Peter I. By a decree of 1699, it was decided to involve Russians in military service on a permanent basis, and in 1705 the term recruit was defined - a person who is called up to serve in the army
. True, the service life was not established; more precisely, it was stated “as long as strength and health allow.”
The following were called up for military service:
- the officers
are nobles; - The soldiers
included burghers and peasants.
Each community had to submit to the army a man whose age was from 20 to 35 years, for every 20 households
. The number of households could change due to the situation in the country and the need to recruit recruits.
Since 1732, when Anna Ioannovna was in power, the conscription age and length of service in the army have changed. From that time on, teenagers and men aged 15 to 30
. The length of service in the army was limited to years - for junior ranks it was less than 10 years. The length of service depended on the rank, in addition, if a peasant in the service sought a promotion (the rank of officer), then he was transferred to another class - the nobility.
Four years later, in 1736, another condition was introduced that affected recruits. The only sons in the family were exempt from military duty.
Since 1762, a general period of military service has been established. It was 25 years for all recruits, regardless of their rank. But the following were exempted from military duty:
- nobles;
- merchants;
- honorary citizens;
- spiritual class.
Thus, from 1762 to 1808, only peasants and townspeople
.
New changes in the composition of recruits and length of service were made in 1808 and lasted until 1815. Then, on the territory of the Russian Empire, special military settlements were created in which peasants lived. These settlements also housed regiments of soldiers with their families. Male residents of settlements became cantonists from the age of 7, that is, they began to bear military duty for life.
This approach was quite cruel, so in 1834 it was decided to establish a strict service life of 20 years.
. After this, the soldier went into reserve. From 1839, the length of service in the army began to decrease and by 1859 it was 12 years for all military personnel. Men under the age of 40 were accepted into the army.
How to write a report?
In accordance with paragraph 12 of Art. 34 of section VIII of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of September 16, 1999 No. 1237, the dismissal of a military personnel is carried out on the basis of a report submitted by him . The only exceptions are those situations when such a decision is made without taking into account his will (in this case such a document will not be required).
At its core, a report is analogous to a statement that citizens write if they want to terminate their employment relationship with their employer. Today there is no strictly established sample of such a document. It is compiled in free form.
The finished report is reviewed by a special commission, as a result of which a decision is made to satisfy it or refuse dismissal. The review period should not exceed 30 days (clause 116 of Chapter 6 of Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of November 10, 2007 No. 1495).
The most common valid reasons for a serviceman leaving his current service are health conditions, reaching the age limit (for such activities) or family circumstances. Management makes a decision on dismissal or refusal based on the submitted report.
Military service: how long did you serve?
In 1873, a new reform was carried out, which provided for military service. The conscription system was replaced by universal conscription in 1874. From that time on, all men over 21 years of age were accepted into the army. Exclusions based on male class were abolished (with the exception of the clergy). All those liable for military service drew lots, which determined their “fate,” that is, whether a man would join the army or not.
The period of military service was conditionally divided into 2 parts:
- 7 years of service in the ranks;
- 9 years left.
Being in reserve meant the soldier's return home. But he could be called up for training camps for up to 6 weeks no more than 2 times during the reserve period
.
For the navy, the period of military service was different:
- 7 years of service;
- 3 years left.
After this, those liable for military service were enlisted in the militia until the age of 40.
The militia lived at home
, did not attend training camps. They could only be called up during military operations.
The following were exempted from active service (7 years in service):
- the only breadwinner if the family has young children;
- only sons;
- conscripts whose older brothers have already served or are serving in the army.
Such persons liable for military service were automatically enlisted in the reserves for 15 years.
, and then - into the militia.
During real service (7 years in service), men were taught to read and write. Therefore, depending on the available education, the length of service in the army was reduced:
- for those who have completed primary school – up to 4 years;
- for graduates of city schools – up to 3 years;
- for men with higher education – up to 1.5 years.
If a man with a higher education wanted to join the army for real service (formation) voluntarily, then the service life was halved and amounted to 3.5 years
.
Certificate of attendance for military service in 1884
Such rules were in effect until mid-1888. Since June 1888, new changes were made to the collection of laws of the Russian Empire. From that time on, the period of military service was 18 years.
, of which the man was in active service for 5 years and in the reserve for 13 years. The age of a man who was in the militia was raised from 40 to 43 years. Military service was also determined by lot.
For those men who received higher and secondary education or went to serve voluntarily, the period of active service was increased by 2-4 times
In 1906, a provision regarding service in peacetime appeared. Thus, from April 1906, in peacetime, they served in the ground forces (in the ranks) by lot for 3 years. Next, those liable for military service were enlisted in the reserve category I and II for 7 and 8 years, respectively.
.
Reserve category I - serviceman's age is 24-31 years. Such men, after active service, were sent to the field troops. Reserve category II - age 32-39 years. Men in the II category reserve were intended to staff reserve troops and rear institutions. The maximum age for those enlisted in the reserve should not exceed 43 years.
Duration of active service
in other troops (not artillery and infantry) was 4 years, after which the serviceman was sent to the 1st category reserve for a period of 7 years, and to the 2nd category reserve for 6 years.
If the soldier served in the navy
, then the period of active service was 5 years, the service life in the 1st category reserve was 3 years, and the 2nd category reserve was 2 years.
Also, benefits were provided for soldiers depending on their education. Those who completed 6 classes of a gymnasium or a course of a 1st category educational institution served in the army (in the ranks) for 2 years and were in the reserve for 16 years.
If a man wanted to voluntarily serve in the army, he had to reach the age of 17 and complete courses at an educational institution of the 1st or 2nd category or pass a special exam upon entering the service.
The terms of service of volunteers were:
- for a graduate of an educational institution of the 1st category - 1 year of active service and 12 years in reserve;
- for a graduate of an educational institution of the second category - 2 years of active service and 12 years in reserve.
If a person liable for military service was not healthy, then he was given a deferment from performing military service until he fully recovered. Provided that the man was completely unfit for service (unable to walk or have other illnesses), he was completely exempt from military service.
If a man studied, a deferment until graduation
. In case of property problems (building a house) – 2 years. Benefits for the only son in the family and the sole breadwinner have also been preserved. Clergymen were completely exempt from military service, and doctors of medicine were immediately enlisted in the reserves.
Composition of the army during the First World War
In wartime, or more precisely during the First World War, all those liable for military service and men who were in the reserve and militia were recruited to serve
. The age of the men ranged from 20 to 43 years.
In addition, recruits aged 21 were called up for service during the First World War. Since 1916, recruits began to be called up for service at the age of 19 due to hostilities.
In addition, all free riders who were capable, but had previously received benefits from military service, were called up for service.
An estimated 15.5 million men were conscripted into service during the fighting of World War I
.
Procedure and rules for repaying a military mortgage after dismissal
When planning to leave the service, citizens are interested in how military mortgages are paid after leaving the army. Targeted housing loans are provided to military personnel on favorable terms.
It provides housing for a subject performing military duties. In this case, the financial burden caused by the repayment of the mortgage loan is borne by the state.
Sometimes, upon early termination of military service, the discharged subject has to close this loan on his own. This depends on the reason for the person leaving the armed forces.
Military service in the USSR
In 1925, the USSR law on compulsory military service was adopted. The duration of military service was 2 years for Red Army soldiers and 3 years for junior officers.
red navy and aviation. The call was made annually.
In September 1939, a new USSR Law “On General Military Duty” was adopted. According to it, boys who turned 19 in the year of conscription could be drafted into the army. If a guy had already graduated from school or a similar educational institution, then he could be drafted into the army at the age of 18.
The length of service depended on the rank and military composition:
- 2 years - ordinary ground forces;
- 3 years – junior commanding officers of the ground forces, privates and junior commanding officers of the Air Force;
- 4 years – privates and junior commanding officers of the coast guard and border fleet;
- 5 years – privates and junior commanding officers of Navy ships.
Since 1941
conscription into the army was carried out according to wartime rules. See next point.
In the post-war period, that is, from 1946 to 1948, there were no conscriptions into the army. All conscripts were engaged in restoration work in mines, mechanical engineering enterprises and construction sites.
In 1949, the rules for conscription and military service were changed. According to the new law, recruits were called up once a year in November or December. The service life was:
- 3 years – for aviation and ground forces;
- 4 years - for the fleet.
The last time during the Soviet period the terms of military service were changed at the end of 1967
. Thus:
- military personnel of any rank and troops with higher education - 1 year;
- soldiers and sergeants of the Soviet Army, border and internal troops, coastal units and Navy aviation - 2 years;
- sailors and foremen of ships and coastal units of the Navy and maritime units of border troops - 3 years.
In addition, since 1967, conscription into the army began to take place twice a year.
.
In what cases can a military resignation order be canceled?
In some situations, the order to dismiss a military personnel may be cancelled. As a rule, this applies to the following cases:
- The serviceman was deprived of his position for unfounded reasons - in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 23 Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the Status of Military Personnel”, a person whose rights were violated must be restored to his previous position, and with his consent transferred to another place (equal or lower in status). In addition, he must be compensated for losses caused as a result of the decision illegal decision, including compensation for moral damage (in this case, an official decision of a judicial authority will be required). These rules apply to military personnel working under a contract. According to the current procedure, when a serviceman leaves, two orders are issued: dismissal and expulsion from personnel. Thus, if it is determined that the reason for removal from the position is unfounded, then both orders will have to be canceled.
- During the dismissal procedure, any violations were committed - a typical example of such a situation is exclusion from personnel until full settlement with the serviceman has been made (payment of salary, provision of food and clothing). In this case, only the order that concerns exclusion from personnel. In this case, the dismissed person must be reinstated and remain in military service until all violations committed are eliminated.
In general, it can be noted that a serviceman has the right to appeal against illegal actions of management related to dismissal in the following authorities:
- at higher command;
- in the military prosecutor's office;
- through the court.
The dismissal order will have to be canceled by the official who issued it, or by the serviceman’s direct superior (clause 22 of Section VIII of Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of September 16, 1999 No. 1237).
Composition of the Soviet army during the Great Patriotic War
At the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, men aged 23 to 36 were conscripted
. In July, women began to be partially conscripted into service, class restrictions were also lifted (clergy, officers of the old army, Cossacks and others could be conscripted).
Summons against a woman
Since 1942, military personnel from 17 to 50 years of age began to be conscripted into the army.
. The summons was brought home or left at the village council. The conscript was also released from work and was given money for 2 weeks in advance. At the place of conscription, a person had to come with his head shorn, with documents, clothes and food. For failure to appear or lateness, the conscript could be held accountable.
Deferment of conscription was granted to combine operators and tractor drivers
, who collected crops for local residents and military personnel.
For service in units with a special risk category (paratroopers, tank destroyers, pilots), volunteers aged 18 to 20 years were accepted who had positive characteristics and, preferably, athletes who passed the standards “Be ready for work and defense of the USSR” or “ Ready for the anti-chemical defense of the USSR.”
Teenagers could be accepted as volunteers into divisional detachments
.
Police officers can increase their service to 25 years from 2020
The government of the Russian Federation has not neglected another category of citizens – security officials. The sensational pension reform will most likely affect police officers. Along with raising the retirement age for ordinary Russians, employees of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the FSB, as well as the Russian Guard, are preparing for the changes. The media have already written more than once that the length of service will be increased in 2020, but to date there has been no confirmation of the rumors.
It is important to know: What rules must be followed during work?